Lidarmos: Intelligent LiDAR Mapping System Transforming Spatial Data
Introduction to Lidarmos
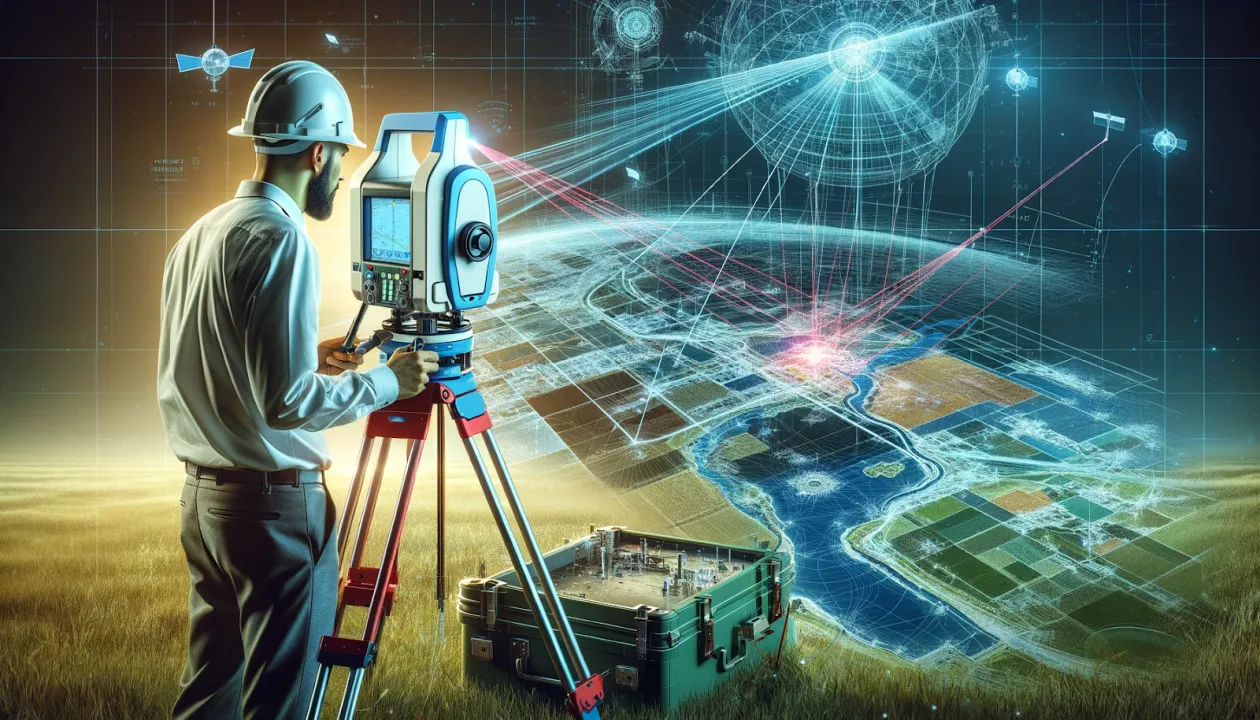
Lidarmos is an emerging concept that represents the next generation of LiDAR-based mapping and sensing systems. Built on the core principles of LiDAR technology, lidarmos focuses on transforming raw laser scan data into highly accurate, real-time spatial intelligence. In a world increasingly driven by automation, smart infrastructure, and data-led decisions, lidarmos stands as a powerful framework that bridges physical environments with digital understanding.
Unlike traditional LiDAR usage that often ends at static 3D maps, lidarmos emphasizes continuous mapping, interpretation, and operational use of LiDAR data. It is designed not only to measure distances but also to support intelligent systems that rely on precise awareness of their surroundings. From smart mobility to urban planning and environmental monitoring, lidarmos plays a critical role in enabling machines and systems to “see” the world with clarity and depth.
Understanding the Core Concept of Lidarmos
At its foundation, lidarmos can be understood as a LiDAR mapping and operational system that integrates hardware, software, and data intelligence into a unified workflow. It goes beyond simple point cloud generation by focusing on how LiDAR data is processed, updated, analyzed, and used in real-world applications.
Lidarmos operates on the principle that spatial data should be dynamic and actionable. Instead of producing one-time scans, the system supports ongoing data capture and interpretation. This allows environments to be monitored as they change, making lidarmos especially valuable for industries where conditions evolve rapidly, such as transportation networks, construction sites, and urban infrastructure.
How Lidarmos Works in Practice
The lidarmos workflow begins with LiDAR sensors emitting rapid laser pulses toward surrounding objects. Each pulse reflects back to the sensor, allowing the system to calculate distance with extreme accuracy. These measurements are combined with positioning and motion data to create a dense three-dimensional representation of the environment.
What differentiates lidarmos is the way this data is handled after collection. Advanced algorithms clean, classify, and structure the point cloud data, identifying surfaces, objects, and spatial relationships. The system then converts this information into usable digital models that can be updated continuously. This real-time or near-real-time processing ensures that the digital representation always reflects the current state of the physical world.
Lidarmos as a Spatial Intelligence Platform
Lidarmos is best described as a spatial intelligence platform rather than just a mapping tool. It interprets LiDAR data to provide insights that support decision-making. By understanding elevation, depth, and object movement, lidarmos enables systems to react intelligently to their surroundings.
This spatial intelligence is essential for automated and semi-automated technologies. Machines equipped with lidarmos-based data can identify obstacles, analyze terrain, and adapt to environmental changes without relying solely on human input. This capability positions lidarmos at the center of modern smart systems.
Applications of Lidarmos in Smart Mobility
One of the most impactful applications of lidarmos is in smart mobility and transportation systems. Accurate and up-to-date spatial data is crucial for modern mobility solutions, especially those involving automation and shared infrastructure. Lidarmos provides the detailed environmental awareness needed for vehicles and mobility platforms to navigate complex urban spaces safely.
By continuously mapping roads, intersections, and surrounding objects, lidarmos supports safer navigation and better traffic management. It helps identify hazards, monitor road conditions, and adapt routes based on real-world changes. As cities move toward smarter transportation networks, lidarmos becomes a foundational technology enabling efficiency and safety.
Lidarmos in Urban Planning and Smart Cities
Urban environments are dynamic systems that require accurate data to plan and manage effectively. Lidarmos plays a key role in smart city development by offering high-resolution 3D models of buildings, streets, and public spaces. These models allow planners to visualize urban growth, analyze infrastructure needs, and design sustainable solutions.
Because lidarmos data can be updated regularly, city authorities can monitor construction progress, detect unauthorized changes, and assess the impact of new developments. This ongoing insight supports data-driven urban governance and helps cities respond proactively to challenges such as congestion, flooding, and population growth.
Environmental Monitoring with Lidarmos
Environmental monitoring is another area where lidarmos delivers significant value. Natural landscapes are constantly changing due to climate, vegetation growth, and human activity. Lidarmos enables precise tracking of these changes over time by capturing accurate elevation and surface data.
Through repeated scans, lidarmos can identify subtle shifts in terrain, measure vegetation density, and monitor erosion or land degradation. This information is critical for environmental protection, resource management, and disaster preparedness. By providing reliable spatial data, lidarmos supports informed decision-making in environmental science and conservation.
Lidarmos in Surveying and Construction
Traditional surveying methods often require extensive manual effort and time. Lidarmos streamlines this process by delivering fast, accurate, and comprehensive spatial data. Construction projects benefit from detailed site models that improve planning, reduce errors, and enhance safety.
With lidarmos, project teams can monitor progress, compare designs with real-world conditions, and detect deviations early. The ability to capture and analyze spatial data frequently ensures that construction activities remain aligned with plans and regulatory requirements. This efficiency leads to cost savings and improved project outcomes.
Advantages of Lidarmos Over Conventional Mapping Systems
One of the main advantages of lidarmos is its level of accuracy. LiDAR-based measurements provide centimeter-level precision, making lidarmos far more reliable than many traditional mapping techniques. This accuracy is critical in applications where even small errors can have significant consequences.
Another key advantage is adaptability. Lidarmos systems can operate in various lighting conditions and environments, including low-light or complex urban settings. The technology does not rely on ambient light, allowing it to function consistently across different scenarios. This reliability makes lidarmos suitable for demanding operational environments.
Data Processing and Intelligence in Lidarmos
The true power of lidarmos lies in its data processing capabilities. Raw LiDAR data is vast and complex, but lidarmos transforms it into structured information that can be easily interpreted. Machine learning and advanced analytics play a role in identifying patterns, classifying objects, and predicting changes.
By integrating intelligence into the data pipeline, lidarmos enables proactive insights rather than reactive analysis. Systems can anticipate potential issues, such as structural weaknesses or environmental risks, before they become critical. This predictive capability enhances safety and operational efficiency across industries.
Scalability and Integration of Lidarmos Systems
Lidarmos is designed to scale across different project sizes and environments. Whether applied to a single construction site or an entire metropolitan area, the system can adapt to varying data volumes and complexity. This scalability ensures that lidarmos remains relevant as projects grow and evolve.
Integration is another important aspect of lidarmos. The system can work alongside other technologies, including geographic information systems, traffic management platforms, and digital twins. By serving as a reliable source of spatial data, lidarmos enhances the effectiveness of these interconnected systems.
Challenges and Considerations in Lidarmos Adoption
While lidarmos offers significant benefits, adopting the system requires careful planning. High-quality LiDAR sensors and data processing infrastructure represent an investment, and organizations must ensure they have the expertise to manage and interpret the data effectively.
Data storage and management are also important considerations, as LiDAR datasets can be large. Lidarmos implementations must include strategies for efficient data handling and long-term accessibility. Addressing these challenges ensures that the system delivers maximum value over time.
The Future Potential of Lidarmos
The future of lidarmos is closely tied to the growth of automation and smart technologies. As autonomous systems become more common, the demand for precise and reliable spatial intelligence will continue to rise. Lidarmos is well-positioned to meet this demand by providing the depth and accuracy required for advanced applications.
Innovations in data processing, artificial intelligence, and sensor technology will further enhance lidarmos capabilities. Faster processing, improved object recognition, and real-time analytics will expand its use cases and impact. Lidarmos is expected to play a central role in shaping intelligent environments of the future.
Conclusion
Lidarmos represents a powerful evolution of LiDAR-based mapping and sensing systems. By transforming raw laser data into actionable spatial intelligence, it enables smarter decisions across mobility, urban planning, construction, and environmental monitoring. Its accuracy, adaptability, and intelligence make it a critical technology in a world increasingly defined by data-driven systems.
As industries continue to seek better ways to understand and manage physical spaces, lidarmos offers a reliable and forward-looking solution. With its ability to deliver continuous, precise, and meaningful spatial insights, lidarmos is not just a mapping system but a foundation for the intelligent infrastructure of tomorrow.